For over a century, lead-acid batteries have been the silent workhorses of the automotive industry, providing the essential spark for internal combustion engines (ICE) and powering various auxiliary systems. Despite the rise of advanced battery technologies, particularly lithium-ion, lead-acid batteries continue to hold a significant and indispensable position in the global automotive landscape. Their reliability, cost-effectiveness, and established recycling infrastructure ensure their continued relevance in an evolving automotive ecosystem.
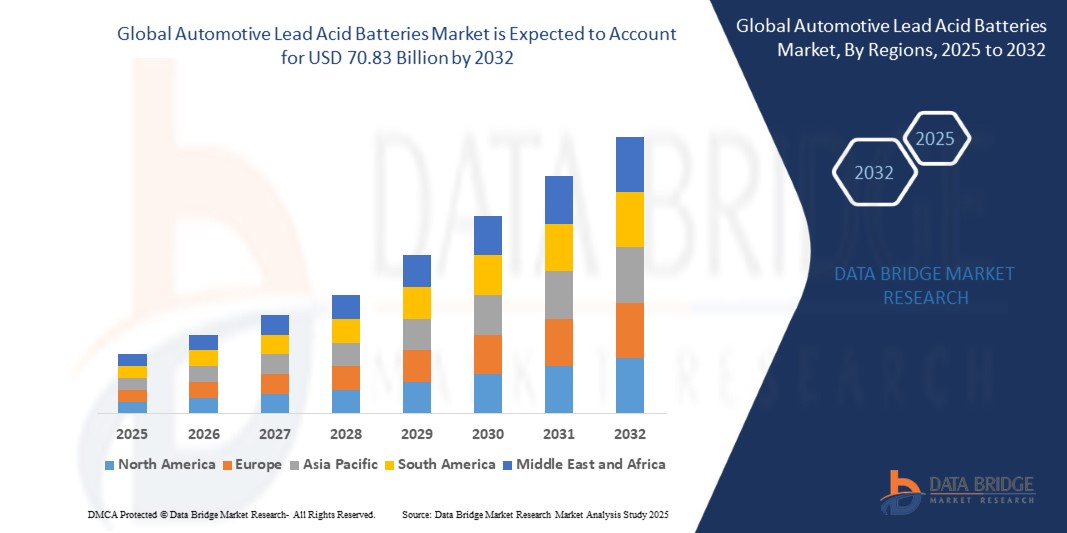
The global Automotive lead acid batteries market size was valued at USD 49.01 billion in 2024 and is expected to reach USD 70.83 billion by 2032, at a CAGR of 4.6% during the forecast period
Access Full 350 Pages PDF Report @
Introduction to Automotive Lead-Acid Batteries
Automotive lead-acid batteries are rechargeable batteries that use lead plates immersed in a sulfuric acid electrolyte to generate electricity. Their primary function is to provide the high burst of power needed to start a vehicle's engine (Starting, Lighting, and Ignition - SLI). Beyond starting, they power the vehicle's lights, infotainment systems, climate control, and various electronic components when the engine is off or idling. Modern advancements have led to different types of lead-acid batteries, including flooded, absorbed glass mat (AGM), and enhanced flooded batteries (EFB), each offering specific advantages in terms of performance, durability, and maintenance. These innovations have allowed lead-acid batteries to adapt to new automotive demands, including vehicles with start-stop technology and even certain auxiliary functions in hybrid and electric vehicles.
Market Size and Growth
The global automotive lead-acid battery market is a mature yet steadily growing sector. In 2024, the market size was estimated to be around USD 25.0 billion. Projections indicate continued growth, with the market expected to reach approximately USD 33.2 billion by 2034, demonstrating a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of around 3.0% during the forecast period of 2025-2034. Other reports suggest the market could reach USD 36.72 billion by 2032, with a similar CAGR. This consistent growth is primarily driven by the sustained production of conventional ICE vehicles globally, the robust aftermarket demand for replacement batteries, and the increasing adoption of micro-hybrid and start-stop technologies in vehicles.
Market Share Dynamics
Asia-Pacific holds the largest share in the global automotive lead-acid battery market. This dominance is attributed to the region's massive and rapidly growing automotive industries, particularly in countries like China, India, and Japan, which contribute significantly to both new vehicle production and aftermarket demand. The high vehicle ownership rates and the need for affordable and reliable energy storage solutions further solidify Asia-Pacific's leading position.
In terms of product type, SLI (Starting, Lighting, and Ignition) batteries continue to dominate the market. These batteries are fundamental for the vast majority of internal combustion engine vehicles on the road. By vehicle type, passenger cars represent the largest segment, driving significant demand for lead-acid batteries. The consistent need for replacements due to the finite lifespan of lead-acid batteries also contributes substantially to the aftermarket segment's share, ensuring a stable demand flow.
Market Opportunities and Challenges
The automotive lead-acid batteries market navigates a landscape of both significant opportunities and persistent challenges.
Opportunities:
Robust Aftermarket Demand: Lead-acid batteries have a typical lifespan of 3-5 years, creating a consistent and substantial aftermarket for replacements. This regular replacement cycle provides a stable revenue stream for manufacturers, regardless of new vehicle sales trends.
Cost-Effectiveness and Reliability: Compared to newer battery technologies, lead-acid batteries remain significantly more affordable and possess a proven track record of reliability. This makes them the preferred choice for budget and entry-level vehicle segments, and for auxiliary functions in even advanced vehicles.
Growth of Start-Stop Systems: The increasing integration of start-stop technology in modern vehicles to improve fuel efficiency and reduce emissions is a major driver. These systems require advanced lead-acid batteries (EFB and AGM) that can handle frequent cycling, creating a growing niche market.
Auxiliary Power in EVs and Hybrids: While lithium-ion batteries power the propulsion systems of electric vehicles (EVs) and hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs), lead-acid batteries are still widely used for low-voltage auxiliary functions such as powering lights, infotainment, and safety systems. This ensures their continued presence in the evolving electrified vehicle landscape.
Established Recycling Infrastructure: Lead-acid batteries boast an exceptionally high recycling rate, often exceeding 95% globally. This well-established circular economy model offers a significant environmental advantage and reduces reliance on virgin lead, making them a more sustainable choice in an increasingly environmentally conscious world.
Emerging Market Expansion: Rapid urbanization and increasing disposable incomes in emerging economies are leading to higher vehicle ownership, especially for conventional ICE vehicles. This fuels the demand for affordable and reliable lead-acid battery solutions in these regions.
Challenges:
Competition from Lithium-Ion Batteries: The rapid advancements and declining costs of lithium-ion batteries pose the most significant long-term challenge. Lithium-ion batteries offer higher energy density, longer cycle life, and lighter weight, making them the preferred choice for primary propulsion in EVs and increasingly for other automotive applications.
Environmental Concerns: Despite high recycling rates, the production and disposal of lead, a toxic heavy metal, continue to raise environmental and health concerns. Stricter environmental regulations and a growing focus on greener alternatives could pressure the lead-acid battery market.
Lower Energy Density: Compared to lithium-ion, lead-acid batteries have lower energy density, meaning they are heavier and bulkier for a given amount of power. This can be a disadvantage in applications where weight and space are critical, such as certain EV designs.
Limited Cycle Life: While advancements have improved their cycle life, lead-acid batteries generally have a shorter cycle life compared to lithium-ion counterparts, leading to more frequent replacements.
Raw Material Price Volatility: Fluctuations in lead prices and other raw materials can impact production costs and profit margins for battery manufacturers.
Market Demand
The demand for automotive lead-acid batteries is fundamentally driven by the global vehicle parc and the continuous need for replacement batteries. Even with the ongoing shift towards electric vehicles, the sheer volume of existing ICE vehicles and their consistent production ensures a steady demand for SLI batteries. Furthermore, the increasing integration of sophisticated electronic systems in modern cars, regardless of powertrain type, necessitates reliable auxiliary power, often provided by lead-acid batteries. The robust growth in vehicle sales in developing economies, where affordability remains a key factor, further underpins the demand for these tried-and-true power sources.
Market Trends
Several key trends are influencing the trajectory of the automotive lead-acid batteries market:
Technological Advancements in Lead-Acid: Manufacturers are continuously innovating to enhance the performance of lead-acid batteries. This includes improvements in grid alloys, plate design, electrolyte formulations, and the development of advanced flooded (EFB) and absorbed glass mat (AGM) batteries. These advancements aim to offer better cold-cranking performance, increased cycle life, improved charge acceptance, and enhanced vibration resistance.
Growing Adoption of Start-Stop Technology: The proliferation of start-stop systems in vehicles to improve fuel efficiency is a significant trend. This drives the demand for specialized lead-acid batteries (EFB and AGM) designed to handle frequent engine restarts without degradation.
Role as Auxiliary Batteries in EVs and Hybrids: Lead-acid batteries are increasingly being used as 12V auxiliary batteries in full electric vehicles and hybrid vehicles. This ensures power for critical safety systems, lights, and infotainment, demonstrating their enduring relevance even in an electrified future.
Focus on Sustainability and Recycling: The automotive industry is increasingly emphasizing sustainability. Lead-acid battery manufacturers are leveraging their established and highly efficient recycling infrastructure as a key environmental advantage, promoting a circular economy approach.
Demand from Commercial and Fleet Vehicles: Commercial vehicles, such as trucks, buses, and delivery vans, heavily rely on lead-acid batteries for their robust starting power and consistent performance, contributing significantly to market demand.
Emergence of Smart Battery Technologies: The integration of smart sensors and monitoring systems with lead-acid batteries is an emerging trend. These technologies allow for real-time monitoring of battery health, charge cycles, and performance, improving operational efficiency and predictive maintenance.
In conclusion, while the automotive industry is undeniably on a path toward electrification, automotive lead-acid batteries are far from obsolete. Their foundational role in ICE vehicles, their adaptation to micro-hybrid and EV auxiliary applications, and their inherent cost-effectiveness and high recyclability ensure their continued importance. The market will see sustained demand driven by replacement cycles, the growth of start-stop systems, and the sheer volume of conventional vehicles worldwide, demonstrating the enduring power and relevance of this established technology.
Contact Us:
Data Bridge Market Research
US: +1 614 591 3140
UK: +44 845 154 9652
APAC : +653 1251 975







Write a comment ...