The Middle East and Africa (MEA) region, traditionally conservative in its approach to substances often associated with recreational use, is witnessing a nascent but significant shift in its perception and exploration of psychedelic drugs. Driven by a growing global understanding of their therapeutic potential, particularly in mental health, this market is slowly but surely gaining traction, albeit amidst a complex regulatory and cultural landscape.
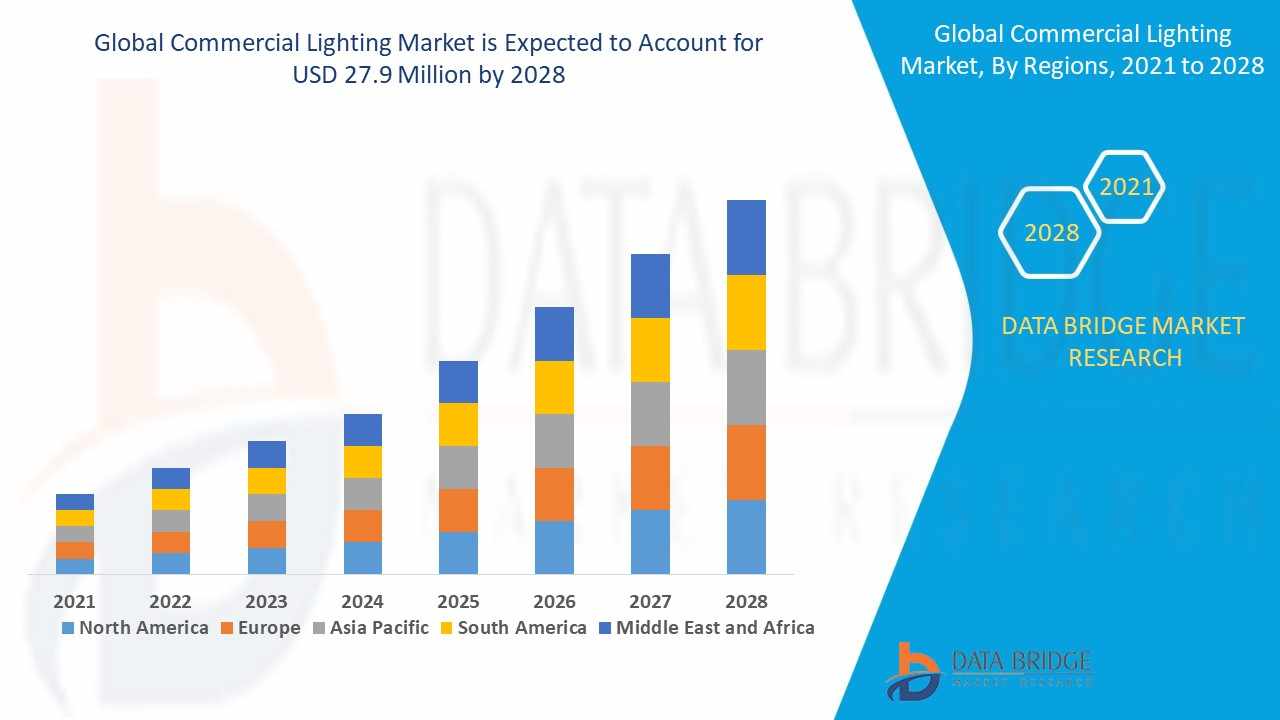
Middle East and Africa market is expected to gain market growth in the forecast period of 2022 to 2029. Data Bridge Market Research analyses that the market is growing with a CAGR of 11.1% in the forecast period of 2022 to 2029 and is expected to reach USD 27.94 million by 2029 from USD 12.14 million in 2021.
Get the PDF Sample Copy (Including FULL TOC, Graphs and Tables) of this report @
Introduction to Psychedelic Drugs
Psychedelic drugs are a class of psychoactive substances that induce alterations in perception, mood, and cognitive processes. Historically used in various spiritual and cultural contexts, modern scientific research is increasingly focusing on their potential medical applications. Compounds such as psilocybin, MDMA (ecstasy), ketamine, and LSD are being investigated for their efficacy in treating a range of mental health disorders, including treatment-resistant depression, PTSD, anxiety, and addiction. The therapeutic model often involves psychedelic-assisted therapy, where the substance is administered in a controlled clinical setting, accompanied by psychotherapy.
Market Size: A Nascent but Growing Segment
While the global psychedelic drug market is experiencing rapid growth, with an estimated valuation of USD 603.1 million in 2024 and projections to reach USD 1.18 billion by 2034 with a CAGR of 7%, the Middle East and Africa represent a smaller, yet promising, portion of this landscape. The MEA psychedelic drugs market was valued at approximately USD 12.14 million in 2021 and is projected to reach USD 27.94 million by 2029, demonstrating a significant CAGR of 11.1% during the forecast period of 2022 to 2029. This growth, though from a smaller base, indicates a rising interest and gradual acceptance of these substances for medical purposes within the region. South Africa, in particular, has shown some openness to alternative therapies, with ibogaine being considered a medication that can be provided by licensed professionals. The UAE is also emerging as a key player, actively exploring the potential of psychedelic-assisted therapies.
Market Share: Mental Health Applications Lead
In terms of application, the market share in MEA, similar to global trends, is predominantly driven by the therapeutic potential of psychedelics in mental health treatment. Conditions such as major depressive disorder, post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), treatment-resistant depression, and opiate addiction are the primary disease indications driving demand. This is a reflection of the global mental health crisis and the increasing search for more effective and sustainable treatment alternatives. Ketamine, due to its existing medical applications and less stringent regulatory hurdles in some contexts, currently holds a significant share. However, as research progresses, other substances like psilocybin and MDMA are expected to gain traction, particularly as their therapeutic benefits become more widely accepted and regulatory frameworks evolve. Synthetic psychedelics are currently the dominant source due to controlled production and consistency.
Market Opportunities and Challenges
The MEA psychedelic drugs market is characterized by a unique set of opportunities and considerable challenges.
Opportunities:
Rising Mental Health Awareness: There is a growing recognition across the MEA region of the prevalence and impact of mental health disorders. This increased awareness is reducing stigma and encouraging a search for innovative and effective treatments, creating a fertile ground for psychedelic therapies.
Growing Research and Development: Global advancements in psychedelic research are demonstrating promising outcomes for various psychiatric conditions. As this body of evidence grows, it provides a scientific basis for advocating for regulatory changes and wider acceptance in the MEA.
Government Initiatives (Pockets of Progress): Certain countries, notably the UAE, are demonstrating a forward-thinking approach to healthcare innovation. The UAE's exploration of psychedelic-assisted therapies, driven by discussions at conferences and interest from sovereign wealth funds, highlights a potential for regulated medical use.
Unmet Medical Needs: For patients who have not responded to conventional treatments, psychedelic-assisted therapies offer a potential lifeline. This creates a strong demand for novel approaches to intractable mental health conditions and addiction.
Potential for Medical Tourism: As some MEA countries, like the UAE, position themselves as medical tourism hubs, the regulated availability of psychedelic therapies could attract patients from other regions with more restrictive policies.
Challenges:
Strict Regulatory Landscape: Many countries in the MEA region have highly stringent drug control laws, classifying most psychedelic substances as illicit with no accepted medical use. This poses a significant barrier to research, clinical trials, and widespread adoption.
Cultural and Societal Stigma: The historical association of psychedelics with recreational drug use and illicit activities contributes to a strong cultural and societal stigma. Overcoming these ingrained perceptions requires extensive public education and careful framing of psychedelics as legitimate medical treatments.
High Cost of Treatment: The specialized nature of psychedelic-assisted therapy, requiring trained therapists and controlled environments, can lead to high treatment costs, limiting accessibility for a large segment of the population.
Limited Clinical Infrastructure: The region currently lacks the established clinical infrastructure and trained personnel necessary to safely and effectively administer psychedelic-assisted therapies on a larger scale.
Lack of Local Research: While global research is progressing, there is limited indigenous research and clinical trials on psychedelic drugs within the MEA, which can slow down local regulatory changes and adoption.
Supply Chain and Sourcing Challenges: Ensuring a consistent and legal supply chain for pharmaceutical-grade psychedelic substances in a highly regulated environment presents logistical and legal complexities.
Market Demand
The demand for psychedelic drugs in the MEA region is primarily an emerging one, driven by the escalating burden of mental health disorders and the limitations of conventional treatments. As awareness about depression, anxiety, PTSD, and addiction grows, and as successful outcomes from international clinical trials become more publicized, there is a nascent but increasing interest from both patients and medical professionals. The demand is currently concentrated in clinical research settings and in very specific, regulated medical contexts where existing treatments have failed. The potential for these drugs to offer profound and lasting therapeutic effects is a key driver for this nascent demand.
Market Trends
Several trends, both global and regional, are influencing the MEA psychedelic drugs market:
Decriminalization and Legalization Discussions: While still in early stages for most of the MEA, the global trend towards decriminalization and medical legalization in countries like Australia (MDMA for PTSD, psilocybin for treatment-resistant depression) and parts of North America is creating a ripple effect. This encourages dialogue and cautious consideration within the MEA.
Focus on Ketamine-Assisted Therapy: Due to its existing legal status and established medical use as an anesthetic, ketamine is currently the most accessible psychedelic for therapeutic purposes in the region. Its rapid antidepressant effects are driving its adoption in specialized clinics.
Academic and Institutional Interest: There is a growing, albeit quiet, interest from academic institutions and medical professionals within the MEA in exploring the scientific validity and therapeutic potential of psychedelics. Conferences and workshops are slowly introducing these topics into mainstream healthcare conversations.
Investment from Sovereign Wealth Funds (UAE): The expressed interest of sovereign wealth funds, such as Abu Dhabi's Mubadala, in investing in biotech firms developing psychedelic medicines, signals a potential shift in economic and policy support for the sector in certain MEA nations.
Telemedicine and Digital Health Platforms (Future Potential): As mental health services increasingly move online, there is a future potential for telemedicine platforms to facilitate initial assessments and follow-up care for psychedelic-assisted therapies, though the administration of the substance itself would remain in-person.
Patient Advocacy and Grassroots Movements: While less overt than in Western countries, a growing number of individuals and groups affected by mental health conditions are advocating for access to alternative therapies, including psychedelics, fostering quiet pressure for policy reform.
The Middle East and Africa psychedelic drugs market is at a pivotal juncture. While significant regulatory, cultural, and financial hurdles remain, the undeniable global momentum in psychedelic research, coupled with a growing regional awareness of mental health needs, suggests a gradual but steady expansion. The trajectory will largely depend on the willingness of governments to adapt existing drug policies, the success of ongoing clinical trials, and continued public education to destigmatize these potentially transformative medicines.
Contact Us:
Data Bridge Market Research
US: +1 614 591 3140
UK: +44 845 154 9652
APAC : +653 1251 975







Write a comment ...